In chemistry texts, reactions and causal relationships are often illustrated with diagrams or pictures. Arrows show the direction of the effect. Diagrams are easiest to understand if you explain the events in the diagram or picture to yourself in complete sentences; you should verbalise them. The noun names of phenomena (evaporation, melting, sublimation) can then be changed into verbs: evaporate, melt, sublimate. How would you explain/verbalise the diagram in the text?
When substances are mixed, reactions can also be described using chemical equations. It is also helpful to verbalise these for yourself.
For example, the reaction equation
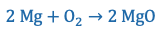
can be used to describe the burning of magnesium. On the left side of the reaction equation are the reactants (magnesium and oxygen) and on the right side are the reaction products (magnesium oxide). Chemical symbols of elements are used in reaction equations, so it is important to know them. In a reaction, the number of atoms always remains the same. Reaction equations can also be illustrated with drawn models:
